|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Constant PI from Fluid Level: |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Constant PI from Fluid Level: |
  
|
Constant PI from Fluid Level
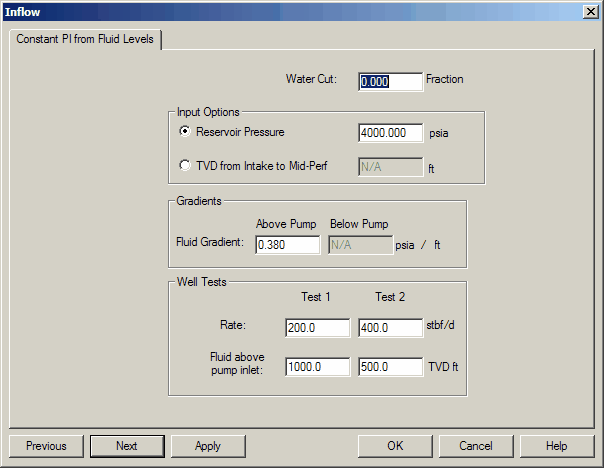
You have two options as to how to enter IPR data using fluid levels. The first option is to provide a reservoir pressure and two fluid levels. The IPR will intersect the pressure axis at the reservoir pressure and drop according to the PI calculated from the two test points. The absolute pressures derived from the two test points are not used since the IPR intersection must hit the reservoir pressure.
Option 1.
RESERVOIR PRESSURE (psia): The average reservoir pressure in the well's drainage area and can be obtained from pressure buildup analysis. This option is limited to one reservoir pressure for all zones.
The second option is to provide an accurate representation of actual fluid levels so that actual pressures can be calculated. To do this the depth from the pump intake to the Mid-point perf, and the gradient below this point must be entered. Remember that gradients above pump intakes are usually 100% oil even in high water cut environments, while the gradient from the intake to the perforations represents your producing fractions.
Option 2.
FLUID GRADIENT BELOW THE PUMP INTAKE (psi/ft): The fluid gradient in the annulus obtained from : G = rho / 144.0. Where: G = fluid gradient (psi/ft) and rho = fluid density (lb/cubic ft).
DEPTH FROM INTAKE TO MPP: This is the TVD distance from the pump intake to the mid point of the perfs as referenced by the reservoir pressure. This value is required to correct pump intake pressures as defined by fluid over the pump to flowing bottomhole pressures.
Common Entries-
WATER CUT: The fraction of the total liquid flow stream that is made up of water. In the results, fluid rate data is reported as TOTAL fluid which includes this water cut fraction.
FLUID GRADIENT ABOVE THE PUMP (psi/ft): The fluid gradient in the annulus obtained from : G = rho / 144.0. Where: G = fluid gradient (psi/ft) and rho = fluid density (lb/cubic ft).
FLOW RATE (mscfd or stbpd): The surface production rate measured in thousand cubic feet or barrels per day at standard conditions.
FLUID LEVEL (ft): The fluid level in the annulus given as the true vertical depth from the pump intake to the top of the fluid interface in TVD ft. It can be obtained by shooting a fluid level with an acoustic recording device (i.e. Echometer) and subtracting that amount from the depth to the pump intake. This definition was changed in June, 1994 to better reflect available field data.